How To Check The Diamond Quality
How To Check The Diamond Quality
Key Highlights:
Cut: Refers to a diamond’s proportions, symmetry, and polish. A well-cut diamond maximizes brilliance and sparkle.
Color: Diamonds are graded from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow/brown). Colorless diamonds are the most valuable.
Clarity: Indicates the presence of flaws. Flawless diamonds are rare, but most diamonds have inclusions invisible to the naked eye.
Carat Weight: Measures the diamond’s weight. Larger diamonds are rarer and more expensive, but cut, color, and clarity also affect value.
Tips:
- Prioritize Cut for brilliance.
- Consider near-colorless diamonds (G-J) for value.
- Aim for eye-clean clarity.
- Balance carat weight with cut quality.
- Get a certification from GIA or AGS.
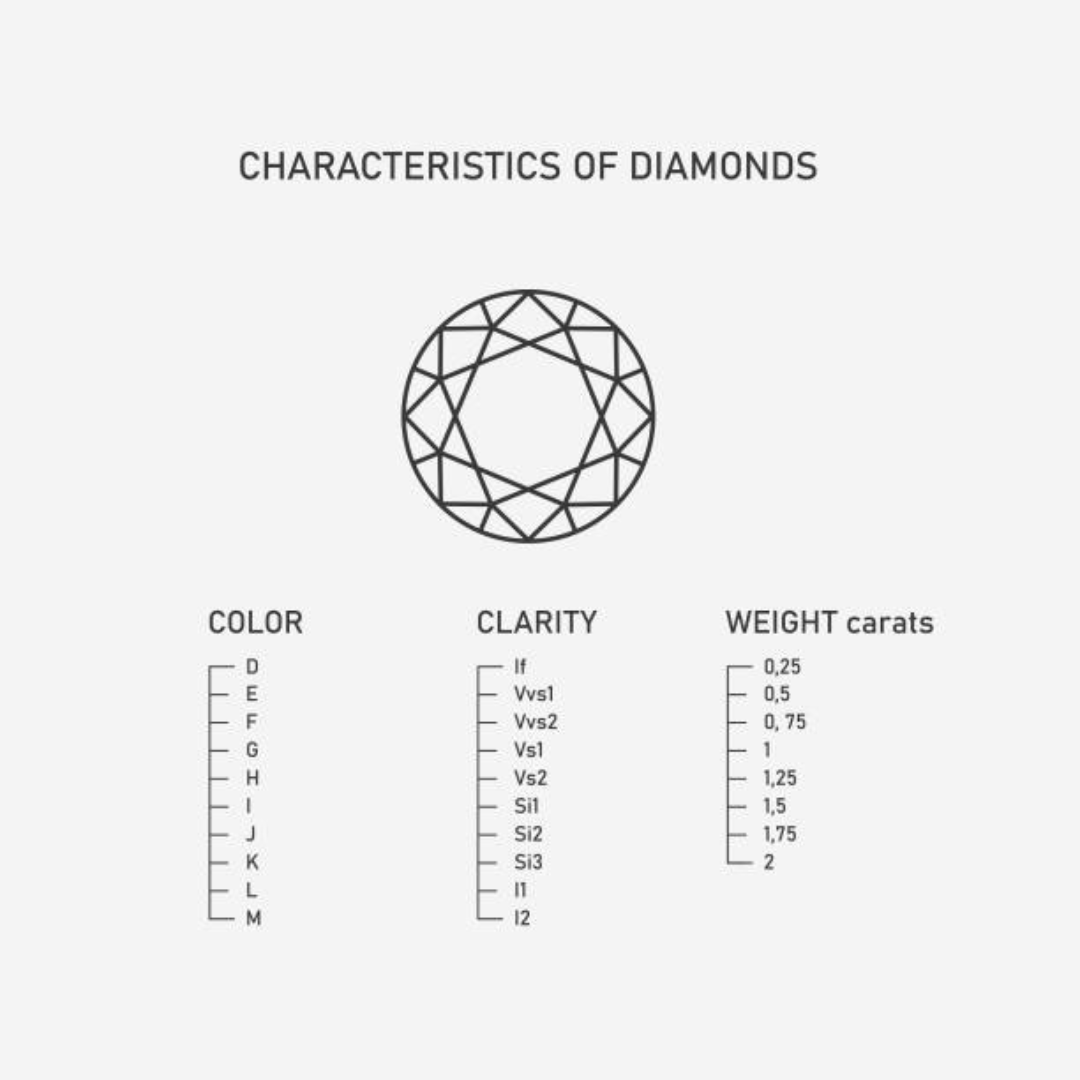
The 4Cs of Diamond Quality
Considering the expense, your buyers and investors want assurance that they’re getting value for money, so there must be a universal standard to measure diamond quality.
Highly trained experts in the niche of diamond evaluation, specialists in the field of diamond appraisal will thoroughly investigate various aspects of each diamond they value using the 4 C’s of diamond quality, namely Carat, Color, Clarity and Cut.
Once these are quantified, a formal certification is drafted and cataloged to the diamond in question.
All of these aspects will determine the brilliance and the fire – the manipulation of light and its spectrum – demanding attention and describing quality.

1. Carat
Carat is the unit of measure describing the weight of diamonds and is by far the most scientifically evaluated aspect of the 4 C’s.
It is calculated using specialized calibrated scales and since it can be said that size matters, the bigger the diamond, the greater the value.
But very important to note is that the other C’s come into play as well, and smaller diamonds can be significantly more valuable if the other aspects outweigh the diamond weight.
Carat weight is traditionally described in fractions and/or multiples of Carats.
But because the metric system has become more universally accepted, Carat weight is more often than not described in decimals, which is far more accurate.
For example, a retail diamond might be traditionally described as 2 Carats, where in actual fact it’s around 1.78 Carats.
This means that your 1.78 Carat gem is more expensive—per carat—than the 2 Carat gem, the other determinants of quality being equal that is.
It works the other way around as well.
A wholesale buyer may value your 1.78 Carat diamond at 1½ Carats, meaning you’re getting less money for value, so to speak. Don’t forget that Carat weight is merely one factor determining value and the remaining aspects must be considered. Each diamond is perfectly unique, (not counting industrial diamonds). Shape can also be deceiving: the Cut of the diamond may skew one’s perception of size.
For example, a Heart Shape diamond may appear larger than a Teardrop Cut of the same Carat weight simply because from the side it appears bigger.
This in itself proves how much information is required to make an accurate determination of a stone’s value. Make sure of the size in terms of weight (carat), but always consider the other C’s as well. As we’ll show you below.


2. The Quality of the Color
The next aspect you need to consider is color.
What hue do you see when looking at the diamond?
There are preferences in the market that determine your stone’s value.
Colorless diamonds are the most highly sought after, and as such are the most expensive, all other things being equal. If any colors are perceived, it immediately impacts the value.
The color scale is used, and it’s based on the Latin letters ranging from D to Z, so you therefore have 23 color shades to use in a stone’s report. For example, there may be a D, G, J, K N, S or Z on a report.
This represents a continuum of colors from perfectly colorless, D, becoming yellower and yellower all the way to Z.
Important fact: note that this grading that lowers the value excludes fancier, oftentimes highly sought after colors, like blue and pink. Their popularity means these hues can actually increase the final cost of the gem.
These days, the most widely accepted color rating, devised by GIA, works as follows based on the standard alphabet:
- D – F: Colorless
- G – J: Near Colorless
- K – M: Faint Color
- N – R: Very light Color
- S – Z: Light Color
You can see there are five subsections in each of these categories.
Remember though that aside from Carat, all other aspects become subjective.
For example, the same stone viewed in different lighting or on different backgrounds will appear different in terms of color.
Even your ring’s setting will make it look different than it did on the counter when you picked it out.
Fun fact:
Women will identify differences in terms of color more often than men do.
The remarkable thing about consumer preference along with subjectivity and the 4 C’s is how it impacts stones’ value.
You can have a large, 5ct stone that is graded ‘R’ and a tiny gem with an ‘F’ rating.
The larger stone may still seem less impressive than the almost colorless diamond.
What is the best way to go about it?
Learn from the professionals before judging a stone’s color:
- Place it on a white surface, such as paper
- Turn it over so it faces down
- Make sure there is ample light in the room
- Now look for color
- Remember to consider the overall look again by viewing it from the top, because that’s how it will be perceived when worn
With all this information about color you’re one step closer to making your decision, but don’t forget the other C’s. And of course, beauty is in the eye of the beholder meaning that particular diamond may fetch higher or lower prices depending on which part of the world they’re sold.
3. Clarity Rating of Your Diamond
Clarity is where it becomes really interesting and is described by various degrees of “inclusions”. In terms of Clarity, a perfect diamond is called flawless, it will have no inclusions. Inclusions appear as “feathers” in the stone. You can often see these with the naked eye and in more severe cases they will even appear as chips or other irregularities on the stone’s surface.
The reason why you don’t want inclusions on your stone is because it affects the aesthetics.
When there’s more inclusions, there’s less clarity. Your stone may have a cloudy look and it won’t produce as brilliant a show of light as clear gems does. More bad news: with more inclusions—less clarity—your stone has a higher risk of breaking, getting chips or developing cracks. This will happen more easily if those inclusions are found around the perimeters of your gem.
So, how do the pros grade a diamond in terms of this C?
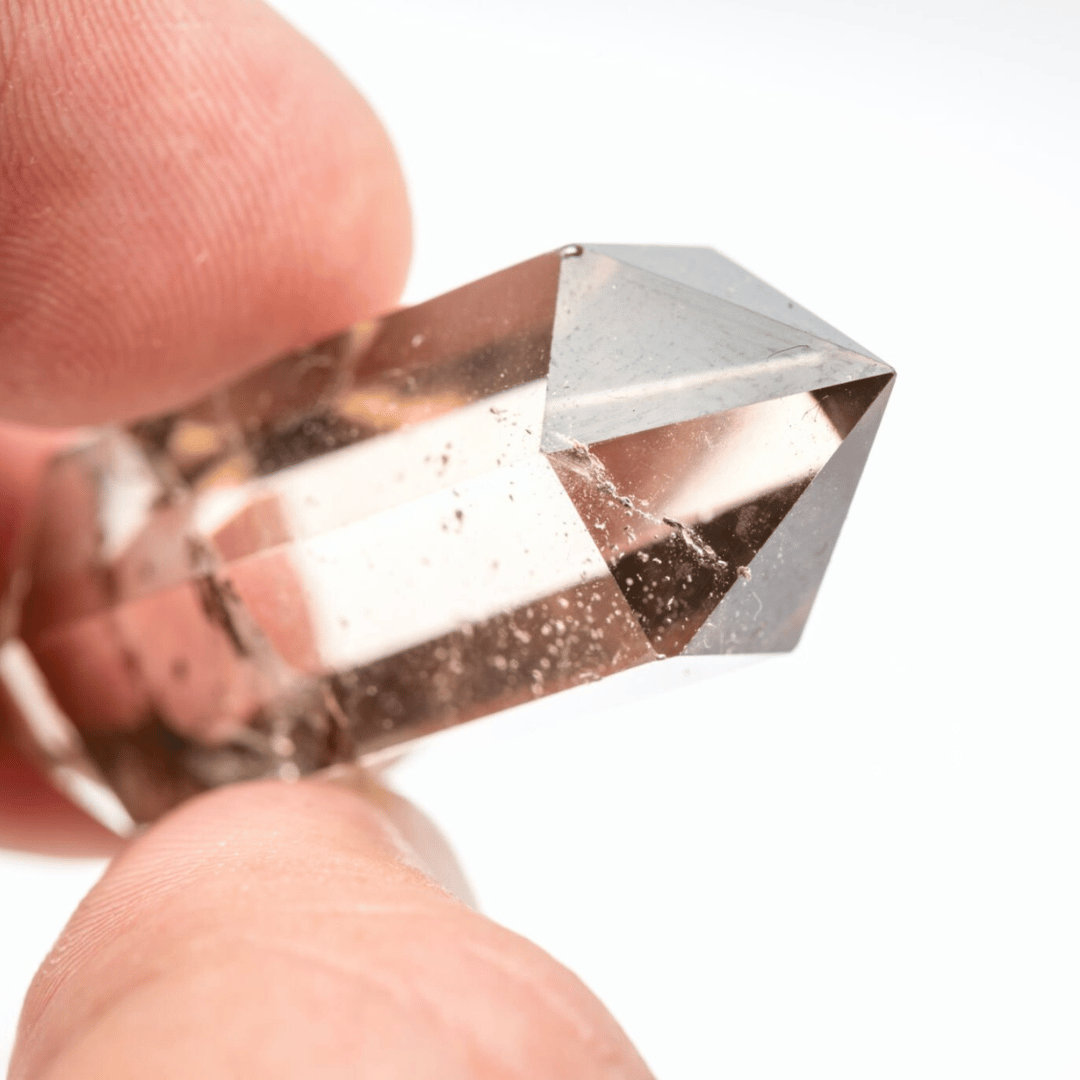

The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) charts Clarity under a 10X magnification as follows:
- FL: Flawless which means you won’t find a blemish or inclusion
- IF: Internally Flawless means there aren’t any internal problems, but there may be a blemish on the outside still
- VVS 1 and 2: Very very slightly Included have tiny problems, but they’re difficult to see
- VS1 and 2: Very slightly Included will have inclusions you’ll see under the microscope, but to the naked eye it will seem flawless
- SI 1 and 2: Slightly Included stones will have inclusions you can see even if you don’t have microscope
- I 1, 2 and 3: Included stones clearly have blemishes and there’s an added concern of the durability of the stone, especially very low on this scale
Diamond value really comes down to rarity: the less abundant the gem, the higher the quality.
Master cutters strive to get the most value out of a diamond and study the gem significantly to determine the best cut.
They’ll strive to get the greatest carat with the least amount of inclusions granting greater value.
But to the naked eye, many diamonds will still appear flawless.
So, commercially it makes sense to include diamonds of lower grade quality in the selection of diamonds on offer at any jeweller.
Why? Because not everyone can afford a $2m gem.
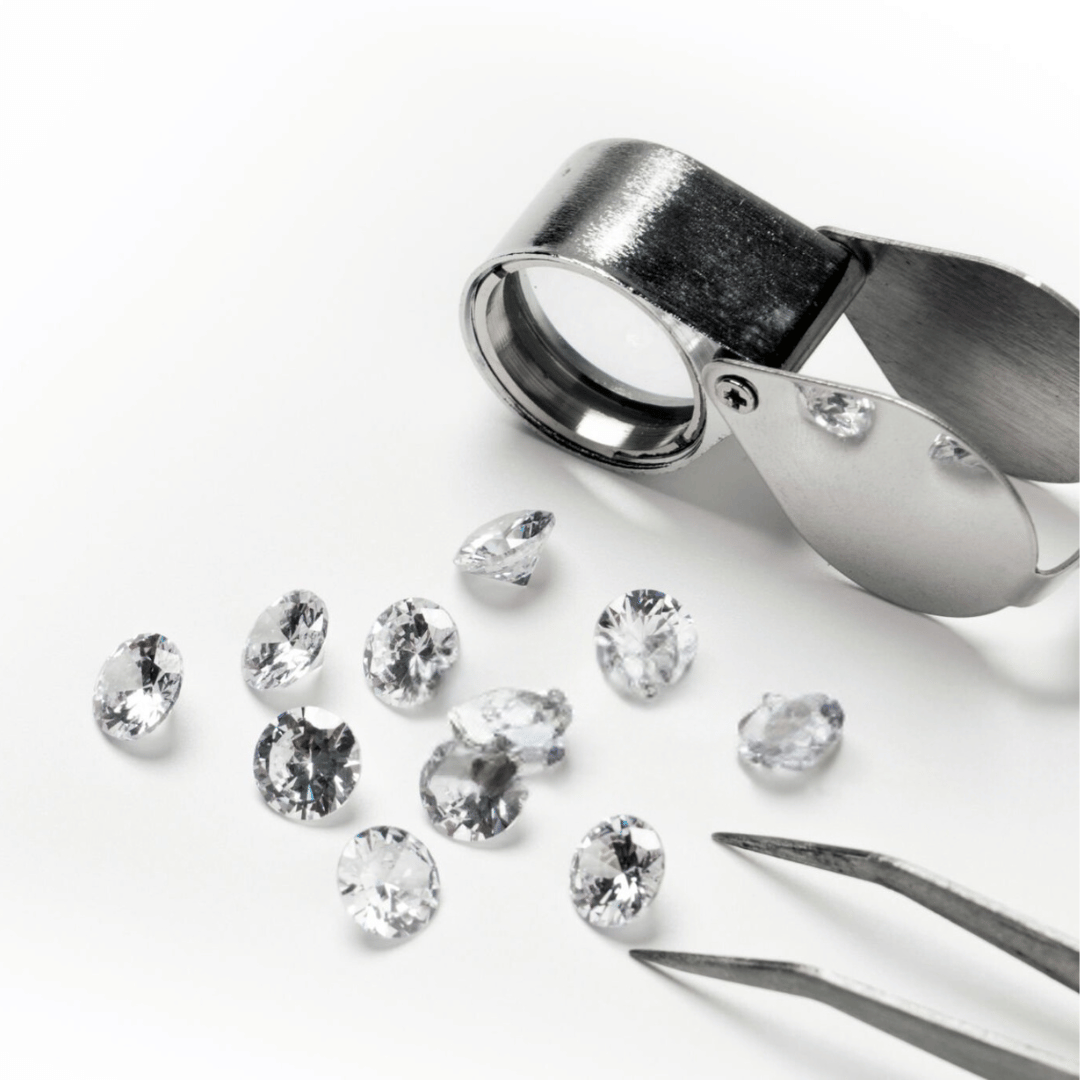
When you are curious about the reality of your stone’s inclusions, simply ask you jeweller for a loupe and have a look.
Be warned:
look at diamonds’ clarity in conditions away from the jeweller’s lighting: those lights are designed to make a stone’s brilliance seem even more impressive—and yes even prevent you from seeing the clarity problems of your potential purchase.
Research the facts about your diamond correctly, so you know what you’re buying.


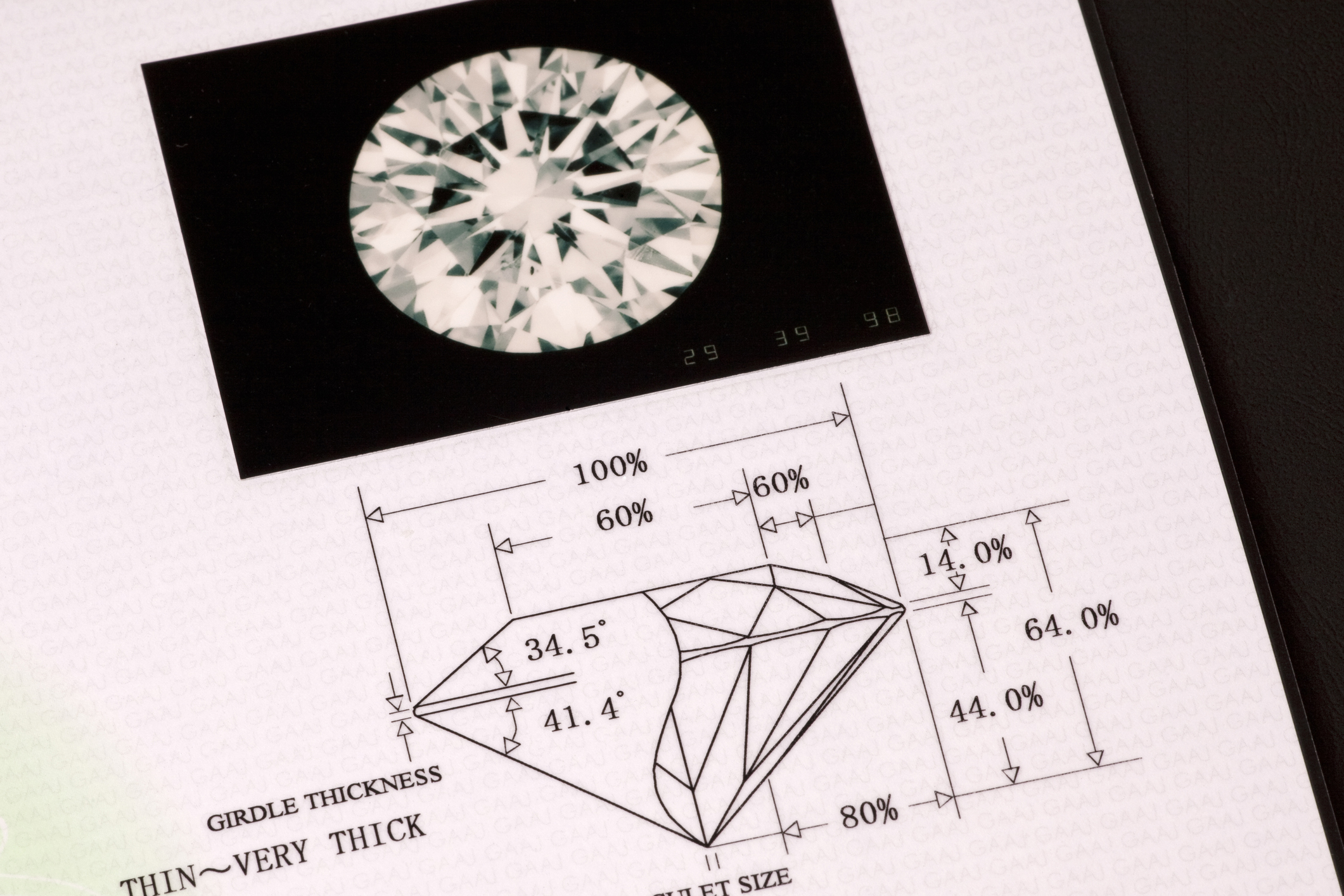
4. Cut Quality of Your Diamond
Depending on the light, the cut is probably the first thing you might notice aesthetically.
It refers to the facets on the surface of the shape.
The facets are the flat surfaces angled around the gem.
Think “pyramid”, but it becomes more complex with more and more facets.
The cut and facet angle, size and arrangement depend on how the cutter wishes to bring the diamond to life.
Cuts that are well balanced with good symmetry disperse light better and will deliver greater brilliance, fire and scintillation:
- Brilliance is the internal and external reflection of light.
- Fire is intermittent flashes of light you’ll see when you turn the diamond in your hands, refracting the light by the various facets.
- Scintillation is the interaction between dark and light areas internally.
The three together will make the diamond appear dull and boring or alive and mesmerizing.
The American Gemological Society (AGS), a world leader in diamond grading standards, use a 10-point scale to describe cut.
Understanding this will help you grasp your stone’s quality & value:
- 0: Ideal
- 1: Excellent
- 2: Very good Cut
- 3 – 4: Good Cut
- 5 – 7: Fair Cut
- 8 – 10: Poor Cut
Note that cut is not exactly the same as when a cutter talks about ‘shape’.
There’s a quality of the cut, and then there’s the shape it was cut in.
Diamonds are generally shaped as round brilliant, the princess, pear, cushion, emerald, oval, and marquise, asscher, heart, and radiant.


Seeing is believing.
Go see the stone in person with your own eyes before making a decision and don’t trust outdated references such as the ‘Holloway Cut Advisor’.
Although these scales exist to measure fire, brilliance and scintillation, a diamond must be experienced to be truly appreciated.
You want to view it from many different angles under varying degrees of light—not only the lights in the jeweler’s store — to uncover its life and appeal.
Yes, you have the right to handle the stone before you buy so you can turn it and view it in many different scenarios.
Judge for yourself how the light plays from within, and how external light is refracted through the diamond.
Only purchase once you’re satisfied.
5. Diamond Certification
Diamonds are also an investment.
All investments need a market standard to record value and diamonds are no different.
Official diamond certification will summarize all of the above aspects concisely recording the date when it was valued and certified.
It’s important that you ask for this documentation, because simply believing your jeweler about the stone’s value isn’t safe.
For one thing, you have no proof of value to insure your investment with your broker and you certainly don’t want to be scammed.


The good news:
These documents are generated by independent role players, not the jewelers themselves.
Diamond certificates will show the shape, the facets and cut, as well as the balance between them.
It will scale the cut and clarity describing the inclusions to be found, if any.
It will show the color and give a brief description of the gem.
Some certificates will go on to include other aspects like polish, fluorescence and symmetry.
Most importantly, it will code the diamond with a GIA (or similar) report number, depending on the grading body the grader belongs to.
Use a reputable body because they govern the determinants of value and are widely respects as leaders in their field.
There are many graders around the world, but grading standards are generally held in highest esteem in the US and Europe:
- Gemological Institute of America (GIA)
- American Gemological Society (AGS)
- European Gemological Laboratory (EGL)
- Diamond High Council (HRD)
- International Gemological Institute (IGI)
- International Confederation of Jewellery, Silverware, Diamonds, Pearls, and Stones (CIBJO)
There’s so much to consider, but once you understand the essence of grading and value described in short herein, you should be well equipped to make the right decision according to your budget. If you’re at all uncertain, you have many options:

- Make sure the report comes from an independent source
- Use the report number on the certificate and contact the relevant body to verify the diamond
- Double check that the person selling the diamond is the current owner
- There is GIA’s online ‘Report Check’ for fast feedback on stones’ details
Do you feel more prepared now that you’re armed with even a basic understanding of diamond value?
The assistance of a reputable gemological laboratory or society will give you assurance and comfort that you’re making a qualified decision when purchasing a diamond.
Conclusion
Selecting a diamond that sparkles for a lifetime requires understanding its value beyond just its size. The 4Cs – Cut, Colour, Clarity, and Carat Weight – work together to determine a diamond’s brilliance and price. Prioritize a good cut for maximum sparkle, consider near colourless grades for excellent value, and aim for eye-clean clarity to balance quality and budget. Remember, a smaller, well-cut diamond can outshine a larger, poorly-cut one. Most importantly, ensure an unbiased diamond certification from a reputable lab like GIA or AGS. With this knowledge, you can confidently choose a dazzling diamond that reflects your love and sparkles forever.